- Plot No. 361/3074 & Plot No 437/3134, Patrapada, BBSR
- +91 9040017001
- +91 8630400500
Understanding Hemophilia: A Rare Yet Serious Bleeding Disorder
What is Hemophilia?
Hemophilia is a rare bleeding disorder where the blood doesn’t clot the way it should. Normally, when we get a cut or injury, our blood forms a clot to stop the bleeding. But in people with hemophilia, this clotting process doesn’t work properly due to the lack of certain clotting proteins called factors.
As a result, people with hemophilia may bleed for a longer time, even from small cuts or injuries. In serious cases, they may experience internal bleeding in joints, muscles, or even in vital organs.
Types of Hemophilia
There are mainly two types of Hemophilia:
- Hemophilia A: Caused by a lack of clotting factor VIII (8)
- Hemophilia B: Caused by a lack of clotting factor IX (9)
Both types are inherited (passed on from parents to children), and they mostly affect males, although females can be carriers.
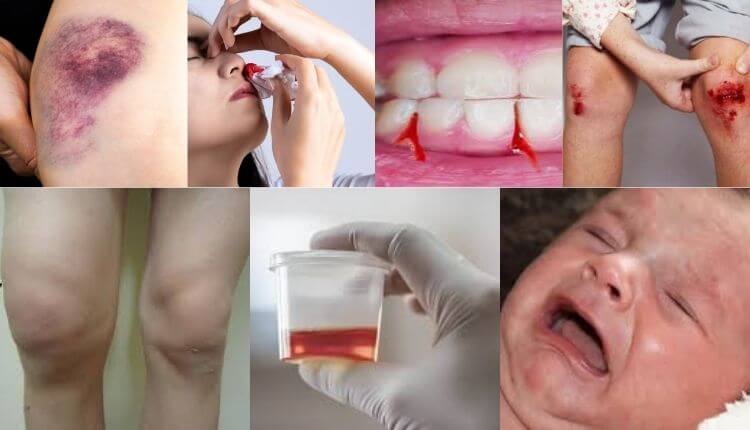
Hemophilia – Common Signs and Symptoms
Hemophilia symptoms can vary from mild to severe. Common signs include:
- Easy bruising
- Frequent nosebleeds
- Bleeding gums
- Prolonged bleeding from cuts or injuries
- Swollen or painful joints (due to internal bleeding)
- Blood in urine or stool
- In infants, unexplained irritability or swelling (due to internal bleeding)
In severe cases, even a small injury can cause serious internal bleeding.
What Causes Hemophilia?
Hemophilia is usually inherited genetically, meaning it runs in families. However, in rare cases, it can also occur without a family history, due to a spontaneous mutation in the clotting factor gene.
It is an X-linked disorder, which means the defective gene is found on the X chromosome. Since males have only one X chromosome, they are more likely to be affected.
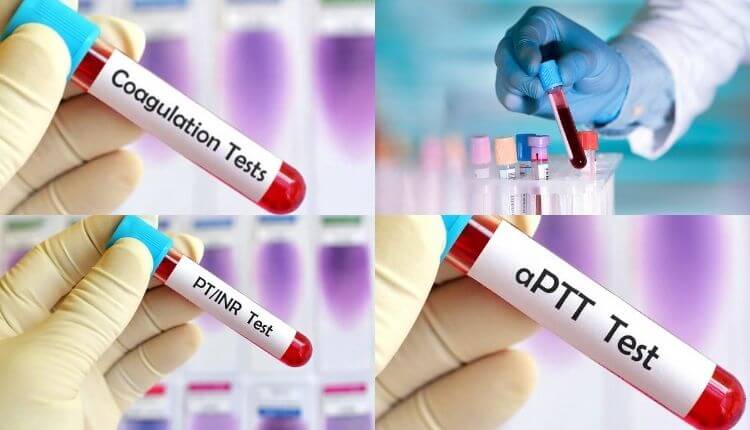
How is Hemophilia Diagnosed?
Hemophilia is diagnosed through blood tests that check the level of clotting factors in the blood. If a person has a bleeding problem, the doctor may recommend:
- Clotting factor tests (assays)
- PT (Prothrombin Time)
- APTT (Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time)
These tests help determine the type and severity of the condition.
👉 If you notice any unusual or prolonged bleeding, consult a doctor and consider getting tested at a reliable diagnostic center.
Can Hemophilia Be Cured?
There is currently no complete cure for Hemophilia, but with proper care and treatment, people with this condition can live a normal and active life.
Treatment options include:
- Replacement therapy: Injecting the missing clotting factor into the bloodstream
- Preventive care: Regular infusions to prevent bleeding episodes
- Lifestyle management: Avoiding activities that can lead to injuries, regular health checkups, and physiotherapy
Living with Hemophilia: Care & Precautions
- Avoid contact sports or risky activities
- Practice good dental hygiene (to prevent gum bleeding)
- Inform your doctor before surgeries or dental procedures
- Keep emergency contact details handy
- Educate friends, family, and schools about your condition
Conclusion
Hemophilia may be rare, but it is a serious condition that requires awareness, early diagnosis, and lifelong care. At Prolife Diagnostics, we are committed to spreading awareness about health conditions like Hemophilia. While we may not treat Hemophilia directly, we encourage early testing and health education for timely care.
🩸 Be aware. Get informed. Stay safe.
If you or someone in your family experiences unusual bleeding, speak to a healthcare provider and consider getting tested.
